What is Generative AI?
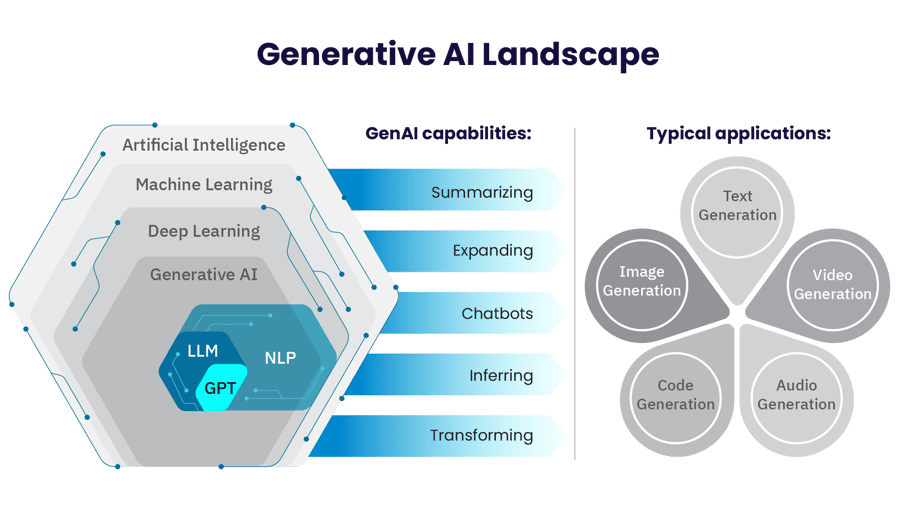
This advancement is already changing the world. But it also brings new complexities that make applying it to your business and navigating implementation challenging.
Critical considerations for implementing Generative AI
Before you determine your initial use cases, you must identify the problems you’ll address, establish clear business objectives, and determine how generative AI will help achieve them. Several other areas must also be covered to ensure success, including:
- Data Availability and Quality: Generative AI depends on data, so the data you need for your use case must be available and meet quality requirements.
- Compliance: You must ensure the use case complies with industry regulations and data privacy requirements, such as PCI DSS, CCPA, GDPR, and HIPAA.
- Ethics and Transparency: It is vital to develop and adhere to specific ethical use principles for your organization’s AI applications and establish clear guidelines for implementation. This starts with ensuring that the data used for training is as unbiased as possible and that the model’s output is regularly audited for fairness. Transparency is critical for tracking how your generative AI models make decisions and generate outputs, both for compliance and to ensure trust and accountability.
- Identify obstacles and quantify the return on investment: Other important areas to consider include uncovering obstacles to success, such as infrastructure and data storage requirements or limited relevant internal skills and knowledge. You should also address scalability across departments or processes, securing sensitive data, and implementing a structure for ongoing updates and maintenance to protect against always-evolving threats. Assessing whether you can realize a worthwhile return on your generative AI investment is paramount.
Four simple use cases to get started with Generative AI
Once you’ve taken the steps necessary to ensure success, you’re ready to experiment with putting generative AI to work.
Many businesses looking at where to implement generative AI can quickly envision dozens of potential use cases across their organization. However, it’s best to start with just two or three use cases where you can have the most significant impact and demonstrate success — so-called “low-hanging fruit.” You can then apply what you’ve learned to future initiatives.
One of generative AI’s most valuable benefits is that it can be customized to meet your precise requirements. Generative AI should be viewed as a flexible, adaptable resource that you can seamlessly integrate into your existing workflows, operations, and customer interactions.
While there are endless potential use cases for generative AI, start where you can most benefit your business within these four applications:
- Streamline data analysis to gain deep insights into critical business functions.
- Automate data processing and analysis to reduce staff time and ensure continuous availability of trusted information.
- Make faster, better decisions that enable your business to evolve and adapt quickly to drive competitive advantage.
- Accelerate innovation by leveraging faster time-to-insights that identify opportunities for new applications.
In our next post, we’ll describe how generative AI transforms manufacturing — and how it can help you do the same for your business.


